Specification
The application can be configured using annotations in YAML. The following sections contain a specification of all keys used to modify existing element types and properties as well as to add new properties.
properties
The key properties defines a list of modified, existing properties of an element type.
Each existing property is specified using the technical name (according to the metamodel).
# Rename existing property 'title'
BusinessAttribute:
properties:
title:
label: Caption
The key label defines the label of the property.
Only properties that are defined in the standard metamodel may be specified and adapted in the list. Properties that are not defined in the metamodel must be configured as customer-specific customProperties.
customProperties
The key customProperties defines a list of new, customer-specific properties of an element type.
Each new property is specified using a technical name.
This technical name must uniquely identify the property and may not conflict with other existing properties of the element type.
# New properties 'confidentiality' and 'priority'
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
confidentiality:
label: Confidentiality
baseType: STRING
priority:
label: Priority
baseType: INTEGER
The key baseType defines the datatype of the property.
New properties become part of the metamodel. In the user interface, they are displayed as input fields for the respective element. New properties are also taken into account in the programming interfaces during import and export.
The key customProperties may only be defined for element types that inherit from Asset in the hierarchy, as well as for Issue.
The technical name of a custom property must start with a letter, : or _ and may further only contain letters, digits, ., :, - or _ but no spaces or other special characters (/, &, ?, <, >, +, =, etc.).
customFunctions
The key customFunctions defines a list of custom functions of an element type.
Each custom function specifies the property href with a link to an external website or application and is displayed in the user interface as an entry in the element's menu.
The external website or application is opened by clicking on the entry in the menu.
Asset:
customProperties:
# Customer-specific property `additionalText`
additionalText:
label: Zusatztext
labelEn: Additional text
baseType: TEXT
customFunctions:
# Custom function to search for the label on the internet
searchGoogle:
label: Google Suche
labelEn: Google Search
title: Suche nach der Bezeichnung in Google
titleEn: Search for the label in Google
icon: brand-google
href: "https://www.google.com/search?q=${this.label}"
# Custom function to translate the customer-specific property `additionalText`
translateAdditionalText:
label: Zusatztext übersetzen
labelEn: Translate additional text
title: Den Zusatztext mithilfe von Google translate übersetzen
titleEn: Translate the additional text using Google translate
icon: language
href: "https://translate.google.com/?sl=de&tl=en&text=${this.additionalText}&op=translate"
In the user interface, custom functions are displayed as entries in the element's menu:
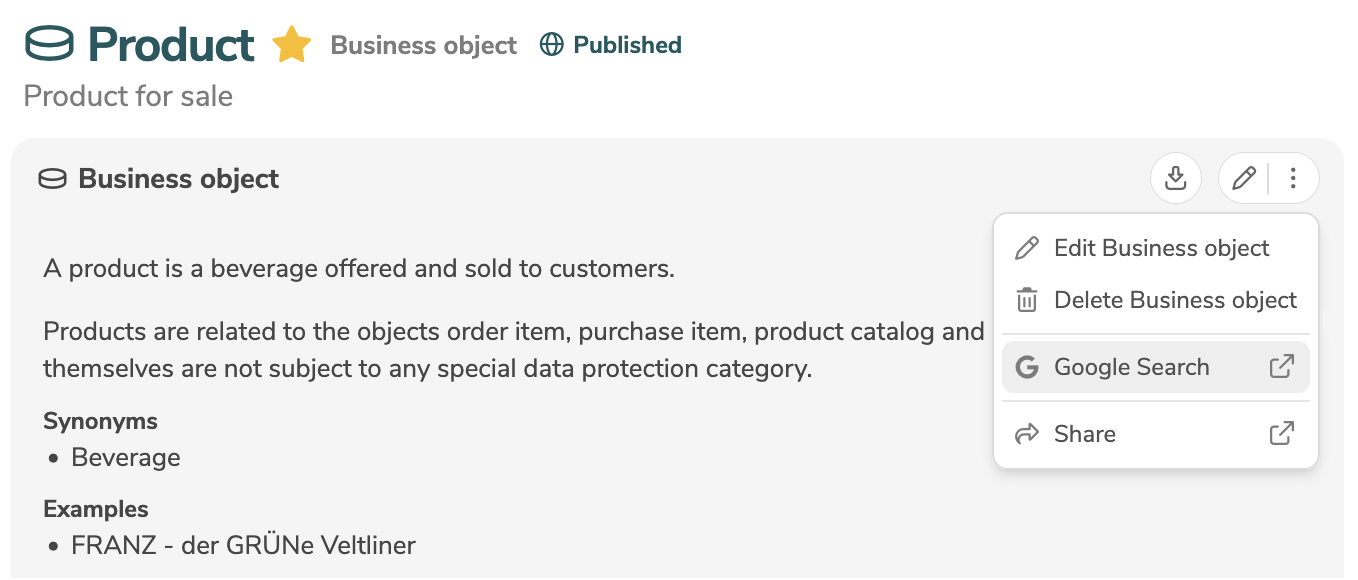
Optionally, the link can be parameterized using placeholders to insert values of the element (e.g. label, additional text) at specific positions.
Placeholders are defined with ${} and refer to a value of the element.
When clicking in the menu of the selected element, the placeholders are replaced by the actual values of the element.
All properties of the element as well as a few other selected values can be specified:
| Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|
${this.*} | By using this. followed by the technical name of a property, all properties that are defined in the standard metamodel (e.g. ${this.label}, ${this.description}, ${this.tags}) as well as all customer-specific properties (e.g. ${this.additionalText}) can be specified. |
${user.userName} | The name of the current user. |
${user.loginId} | The login ID of the current user. |
${tenant.tenantName} | The name of the selected tenant. |
${tenant.tenantId} | The UUID of the selected tenant. |
The entry in the menu is only displayed if all placeholders specified in href can be resolved and have a value.
For example, if the placeholder ${this.additionalText} is specified in href, the custom function is only displayed in the element's menu if the property additionalText in the element is not empty.
label
The key label defines the label of an element type, a property or the value of a list (literals).
The labels are displayed in the user interface (e.g. next to the corresponding input fields or as values in a dropdown list) as well as in the upload/download in Excel and in reports.
In addition to the default language (German), it is possible to specify the label in other languages:
labeldefines the label in German (default language)labelEndefines the label in English
# rename element type 'BusinessAttribute'
BusinessAttribute:
label: Eigenschaft
labelEn: Property
ling: s3p3f
The key ling defines the declension of the label.
The declension is only relevant for labels in German.
# rename property 'title' and define new property 'confidentiality'
BusinessAttribute:
properties:
title:
label: Überschrift
labelEn: Caption
customProperties:
confidentiality:
label: Vertraulichkeit
labelEn: Confidentiality
# define labels of `literals`
Derivation:
properties:
qualifier:
literals:
SPOT:
label: SPOT
labelEn: SPOT
GOLD:
label: Golden Source
labelEn: Golden record
Element types can be stereotyped with the key stereotype.
The keys label and labelEn then define distinct labels for each stereotype.
title
The key title defines the description of an element type, a property or the value of a list (literals).
The descriptions are displayed as tooltips in the user interface (e.g. mouse over the corresponding input fields or values in a dropdown list).
In addition to the default language (German), it is possible to specify the description in other languages:
titledefines the description in German (default language)titleEndefines the description in English
# New property 'confidentiality' with description
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
confidentiality:
label: Vertraulichkeit
labelEn: Confidentiality
title: Die Vertraulichkeitsklassifikation eines Attributs
titleEn: The confidentiality classification of an attribute
Element types can be stereotyped with the key stereotype.
The keys title and titleEn then define distinct descriptions for each stereotype.
icon
The key icon defines the icon of an element type, a property or the value of a list (literals).
The icons are displayed in the user interface (e.g. next to the corresponding input fields or next to the values in a dropdown list).
The application uses icons from the Font Awesome library (version 7.1).
The names of the icons specified in Font Awesome can be used directly in the configuration.
# change icon of element type 'BusinessAttribute'
BusinessAttribute:
icon: unicorn
# define icons of `literals`
Measurement:
properties:
qualityRating:
labelEn: Quality rating
literals:
EXCELLENT:
labelEn: Excellent
icon: traffic-light-go
FAIR:
labelEn: Fair
icon: traffic-light-slow
BAD:
labelEn: Bad
icon: traffic-light-stop
Most icons are available in the styles solid, regular (default), light and thin.
The style is inserted with a hyphen before the name of the icon.
If no style is specified, the style regular is applied automatically.
# change icon of element type 'BusinessAttribute'
BusinessAttribute:
icon: solid-unicorn
To use an icon from the category "Brands", brand is inserted with a hyphen before the name of the icon (e.g. brand-facebook).
Element types can be stereotyped with the key stereotype.
The key icon then defines distinct icons for each stereotype.
If, due to technical reasons, an icon cannot be displayed correctly, it is replaced with the icon .
baseType
The key baseType defines the datatype of a property.
In the user interface, the datatype determines which values can be entered in the corresponding input field.
baseType | Description | User interface |
|---|---|---|
STRING | String | 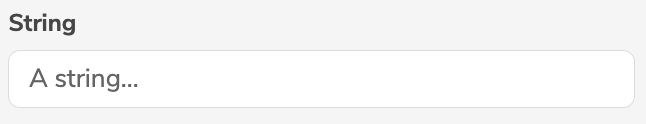 |
TEXT | Formatted Text | 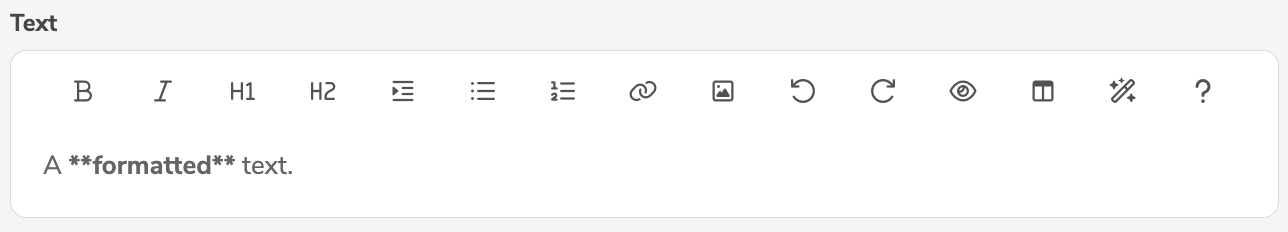 |
DECIMAL | Decimal | 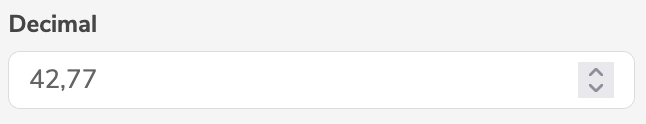 |
INTEGER | Integer | |
BOOLEAN | Boolean | |
BINARY | Binary | 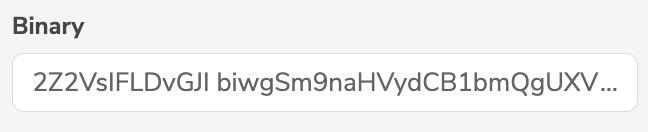 |
DATE | Date | 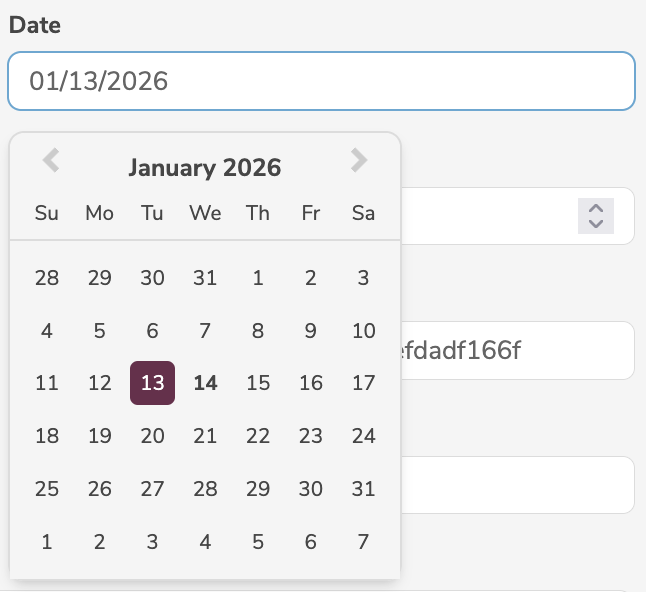 |
TIME | Time | |
DATETIME | Datetime | 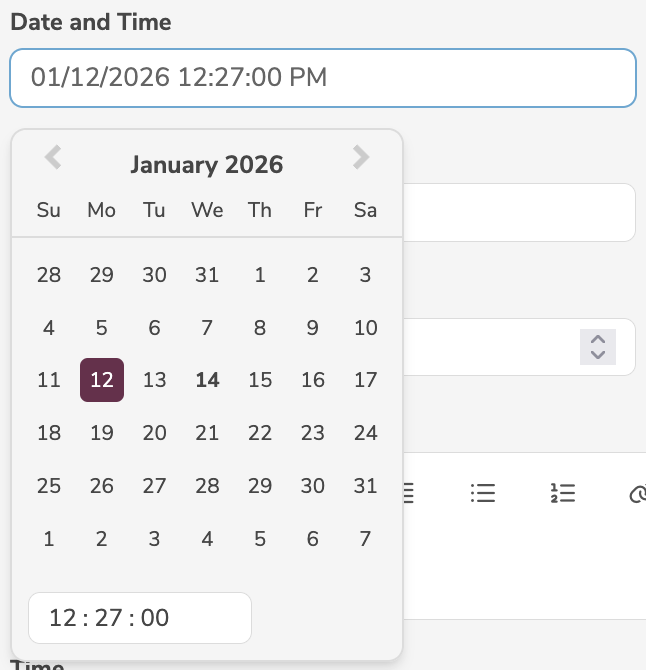 |
DURATION | Duration | 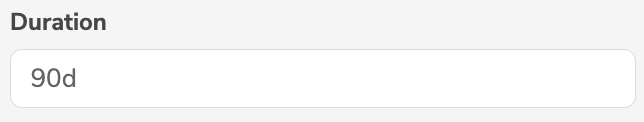 |
CODE | Code | 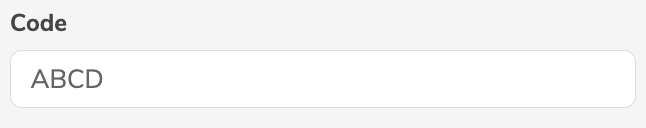 |
ID | Id | 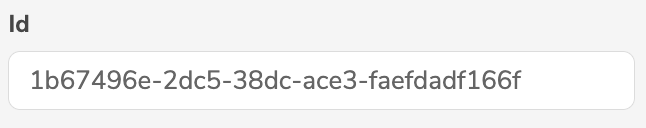 |
# new property 'confidentiality' with datatype `BOOLEAN`
BusinessObject:
customProperties:
confidentiality:
labelEn: Confidentiality
baseType: BOOLEAN
If both the key baseType and the key literals are defined, the key baseType is ignored.
Depending on the baseType, the properties are stored differently in the database.
If the baseType of a specific property is changed, values that were previously stored with the original baseType may not be processed correctly, as their stored value may be incompatible with the new baseType.
Therefore, the values of all affected properties should be deleted before changing baseType.
literals
The key literals defines the list of valid values of a property.
In the user interface, the corresponding input field is displayed as a dropdown list.
Each value has a technical name and label.
The label is displayed in the dropdown list in the user interface as well as in the upload/download in Excel.
The technical name is used in all other interfaces (metadata REST/API, metadata upload/download).
# new property 'direction' with list of valid values
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
direction:
labelEn: Direction
literals:
LEFT:
labelEn: Left
icon: left
order: 1
RIGHT:
labelEn: Right
icon: right
order: 2
It is possible to modify certain existing properties that have already defined literals.
Existing values can be removed or renamed and new values can be added.
The following table lists existing properties that can be overwritten with literals.
| Element type | Property | literals (label) |
|---|---|---|
Processing | lawfulBasis | CONSENT (Consent)CONTRACT (Fulfillment of a contract)LEGAL (Legal obligation)VITAL (Vital interest)PUBLIC (Public interest)LEGIT (Legitimit interest) |
Dataset | accrualPeriodicity | 001 (kontinuierlich)002 (täglich)003 (wöchentlich)004 (14-tägig)005 (monatlich)006 (quartalsweise)007 (halbjährlich)008 (jährlich)009 (nach Bedarf)010 (unregelmäßig)011 (nicht geplant)012 (unbekannt) |
Distribution | format | CSV (CSV)HTML (HTML)JSON (JSON)DOC (DOC)XLS (XLS)RDF (RDF)RSS (RSS)TXT (TXT)XML (XML)PDF (PDF) |
Measure | unitMeasure | NUM (Number Count)YEAR (Years)PC (Prozent)EUR (Euro) |
Measure | calculationDate | EOM (End of month)EOD (End of day) |
Derivation | qualifier | SPOT (SPOT)GOLD (Golden record) |
Composition | qualifier | GROUP (Group)FILTER (Filter) |
Usage | qualifier | IN (Input)OUT (Output) |
Measurement | qualityRating | EXCELLENT (Excellent)GOOD (Good)FAIR (Fair)POOR (Poor)BAD (Bad) |
Person | gender | 0 (not known)1 (male)2 (female)9 (not applicable) |
Enumeration | stringType | ALPHABETIC (Alphabetic)NUMERIC (Numeric)ALPHANUMERIC (Alphanumeric) |
The key literals replaces the entire list for existing properties.
Therefore, all values that should not be deleted must be specified again in the new list.
# remove 'EOM', add 'EOY', keep 'EOD'
Measure:
properties:
calculationDate:
literals:
EOD:
labelEn: End of day
order: 1
EOY:
labelEn: End of year
order: 2
If both the key baseType and the key literals are defined, the key baseType is ignored.
If the key cardinality has the value MANY, the dropdown list in the user interface allows multiple selection.
order
The key order defines the order of properties or values of a list (literals).
The order is taken into account in the user interface (e.g. the order of the corresponding input fields or the values in a dropdown list) as well as in the upload/download in Excel and in reports.
The assigned ordinal number must be unique within the defined values.
# new properties 'priority' and 'confidentiality' with specific order
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
order: 20 # is displayed after 'confidentiality'
confidentiality:
labelEn: Confidentiality
order: 10
The order of existing properties cannot be changed. For new, customer-specific properties, the corresponding input fields in the user interface are always placed after the input fields of existing properties.
In the user interface, the key group allows customer-specific properties to be arranged in groups.
cardinality
The key cardinality defines the cardinality of a property.
The cardinality determines whether a property can hold a single or multiple values.
cardinality | Description | User interface |
|---|---|---|
ONE (default) | The input field allows single selection | |
MANY | The input field allows multiple selection |
# new property 'color' with multiple selection
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
color:
labelEn: Color
cardinality: MANY
literals:
RED:
labelEn: Red
GREEN:
labelEn: Green
BLUE:
labelEn: Blue
Depending on the cardinality, the properties are stored differently in the database.
If the cardinality of a specific property is changed, values that were previously stored with the original cardinality may not be processed correctly, as their stored value may be incompatible with the new cardinality.
Therefore, the values of all affected properties should be deleted before changing cardinality.
width
The key width defines the width of a property.
In the user interface, the width is taken into account when arranging the corresponding input fields.
width | Description |
|---|---|
1 (default) | Two input fields fit next to each other in one line, i.e. the input field occupies only half the width. |
2 | Only one input field fits into one line, i.e. the input field occupies the full width. |
# new property 'priority' mit full width
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
width: 2
If the key baseType has the value TEXT, the key width is automatically set to 2.
defaultValue
The key defaultValue defines the default value of a property.
In the user interface, the corresponding input field is automatically set to the default value, if no value is entered.
# new property 'dataCategory' with default value
BusinessObject:
customProperties:
dataCategory:
labelEn: Data category
defaultValue: master
literals:
transactional:
labelEn: Transactional data
master:
labelEn: Master data
readOnly
The key readOnly [true, false; default: false] defines whether a customer-specific property is read-only.
In the user interface, the corresponding input field is displayed but may only be edited by a user with the access level Administrator.
# new read-only property 'priority'
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
readOnly: true
The key readOnly may only be defined for new, customer-specific properties, but not for existing properties.
hidden
The key hidden [true, false; default: false] defines the visibility of a customer-specific property.
In the user interface, the corresponding input field is not displayed.
However, the customer-specific property is read and written in the interfaces (metadata REST/API, metadata upload/download).
# new hidden property 'priority'
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
hidden: true
Hidden customer-specific properties contain data (e.g. internal, technical or confidential information) that should not be displayed in the user interface, but can be stored and imported and exported in the interfaces.
The key hidden may only be defined for new, customer-specific properties, but not for existing properties.
mandatory
The key mandatory [true, false; default: false] defines whether a customer-specific property is mandatory.
In the user interface, the corresponding input field is displayed as a mandatory field, i.e. the element may not be saved as long as there are empty mandatory fields.
# new mandatory property 'priority'
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
mandatory: true
In the user interface, customer-specific mandatory fields are automatically also displayed in quick add and quick edit.
The key mandatory may only be defined for new, customer-specific properties, but not for existing properties.
If the key baseType has the value BOOLEAN, the key mandatory may not have the value true.
group
The key group defines the group of a customer-specific property.
In the user interface, the corresponding input fields are arranged according to these groups.
The available groups are first defined with the key groups in the element type.
Customer-specific properties can then be specified, referencing the previously defined groups with the key group.
# New groups 'info' and 'additionalData' with properties 'priority', 'caption' and 'confidentiality'
BusinessAttribute:
groups:
info:
labelEn: Information
icon: circle-exclamation
order: 10
additionalData:
labelEn: Additional Data
icon: unicorn
order: 20
customProperties:
priority:
labelEn: Priority
group: info
caption:
labelEn: Caption
group: info
confidentiality:
labelEn: Confidentiality
group: additionalData
In the user interface, the defined groups are displayed while taking into account the labels, icons and order.
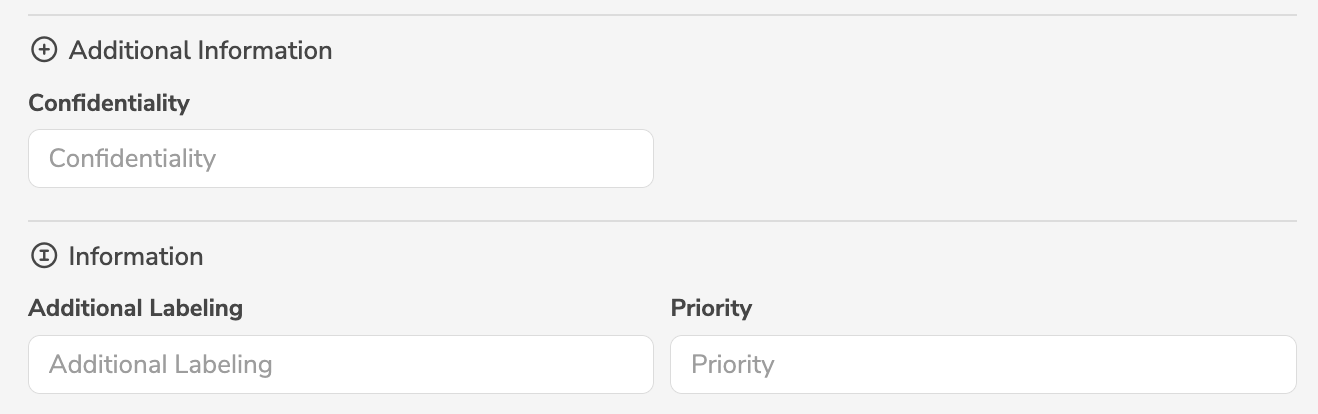
The key group may only be defined for new, customer-specific properties, but not for existing properties.
Some elements (e.g. attributes or measures) have a tab "Computation" in the main panel of the element.
The predefined group computation can be used to display customer-specific properties in this tab:
# Display property 'confidentiality' in tab "Computation"
BusinessAttribute:
customProperties:
confidentiality:
label: Vertraulich
baseType: BOOLEAN
group: computation
stereotype
The key stereotype defines the stereotypes of an element type.
Stereotypes allow element types to be further classified.
In the user interface, the defined stereotypes are automatically displayed as a dropdown list when adding or editing an element.
The key label defines the label of the dropdown list.
The key literals defines the stereotypes, i.e. the entries of the dropdown list.
If a stereotype is selected from the list, then this stereotype is applied to the element.
For each stereotype, distinct labels, descriptions and icons can be defined with the keys label, title and icon.
Furthermore, for each stereotype, existing properties can be modified with the key properties and new, customer-specific properties can be added with the key customProperties.
The label or icon of the stereotype, as well as the modified or added properties, are applied to elements of the element type, only if the respective stereotype is selected.
Thus, there are two ways to configure element types:
- If the customizations (
label,title,icon,properties,customProperties, etc.) are defined directly on the element type, then they are applied to all elements of the element type. - If the customizations (
label,title,icon,properties,customProperties, etc.) are defined per stereotype, then they are applied to all elements of the element type where the respective stereotype is selected.
# stereotypes 'schema' and 'program' for collections
Collection:
properties:
stereotype:
labelEn: Collection type
literals:
schema:
labelEn: Database schema
ling: s1p5n
icon: folder-tree
program:
labelEn: Program
ling: s1p1n
icon: solid-screen-users
customProperties:
sponsor:
labelEn: Sponsor
baseType: STRING
The example defines two stereotypes.
When adding or editing a collection, the dropdown list Collection type with the entries Database schema and Program is displayed in the user interface.
If the stereotype schema is selected, then the collection is presented as Database schema with the icon folder-tree.
If the stereotype program is selected, then the collection is presented as Program with the icon solid-screen-users and additionally with the new, customer-specific property Sponsor.
Stereotypes can be used to configure individual tenant types and icons:
# stereotypes 'base' and 'sub' for tenants
Tenant:
properties:
stereotype:
label: Mandantentyp
labelEn: Tenant type
literals:
base:
label: Basismandant
labelEn: Base tenant
icon: solid-circle-b
sub:
label: Submandant
labelEn: Sub tenant
icon: circle-s
The example defines two stereotypes.
When editing the tenant, the dropdown list Tenant type with the entries Base tenant and Sub tenant is displayed in the user interface.
If the stereotype base is selected, then the tenant is presented as Base tenant with the icon solid-circle-b.
If the stereotype sub is selected, then the tenant is presented as Sub tenant with the icon circle-s.
If a stereotype is changed or deleted, this can lead to lost metadata in customer-specific properties that no longer exist.
Therefore, the values of all properties that no longer exist should be deleted before changing stereotype.
The rule violations automatically check whether a deleted stereotype is still in use anywhere.
ling
The key ling defines the declension class of a label.
The declension determines the formation of the plural and the classification in grammatical cases.
If the label of an element type is defined, the declension class must be specified to ensure the correct presentation of the label in the user interface and in reports.
The declension class is only relevant for labels in German.
# rename element type 'BusinessAttribute' and select correct declension
BusinessAttribute:
label: Eigenschaft
ling: s3p3f
The declension class can be determined as follows. The appropriate values are selected from the columns and are concatenated. The options in columns 1 and 2 refer to the ending used in each of the four cases (nominative, genitive, dative, accusative).
| Singular declension | Plural declension | Umlauts | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|
| s1 -, -s, -, - | p1 -e, -e, .-en, -e | u Use of umlauts | n Neutrum |
| s2 -, -n, -n, -n | p2 -, -, -(n), - | - No use of umlauts | m Maskulin |
| s3 -, -, -, - | p3 -n, -n, -n, -n | f Feminin | |
| p4 -er, -er, -ern, -er | |||
| p5 -s, -s, -s, -s |
The following table with examples is used as an illustration:
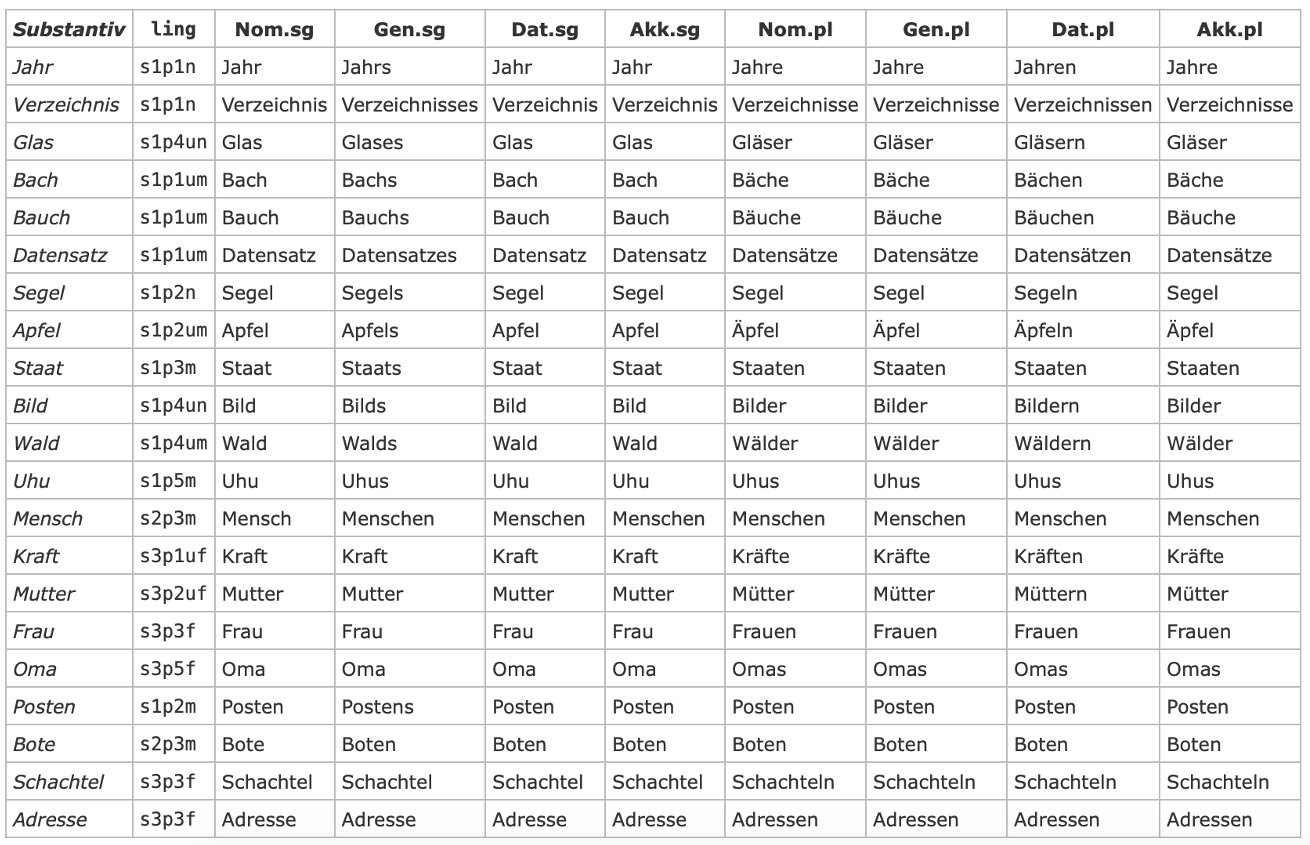
The key plural provides a simplified alternative to the declension class ling.
plural
The key plural defines the plural label of an element type.
The plural label is displayed analogously to the label, wherever the plural form is required.
In addition to the default language (German), it is possible to specify the plural label in other languages:
pluraldefines the plural label in German (default language)pluralEndefines the plural label in English
# Plural
BusinessAttribute:
label: Eigenschaft
labelEn: Property
plural: Eigenschaften
pluralEn: Properties
The key plural provides a simplified alternative to the declension class ling.